Blog

A NJ truck parts distributor was losing money due to wrong inventory counts, slow reports, and no price visibility - all caused by an old MS Access system. Farber Consulting replaced it with a custom ERP inventory software. Stock accuracy jumped from 60% to 98%, purchasing costs dropped 40%, and reports went from 4 hours to 60 seconds in 90 days.
Off-the-shelf inventory software forces you to adapt to its limitations. Custom automated inventory management software adapts to you. This comprehensive guide explores why businesses choose tailored solutions over pre-built tools. Learn about the shortcomings of standard software, including poor integration, limited customization, and scalability issues. Discover how custom solutions transform operations with real-time tracking, mobile access, and seamless integration. We cover essential features like barcode scanning, multi-location support, and automatic reorder points. The guide includes planning tips, budgeting advice, and migration strategies from spreadsheets.

This blog post explains how AI integration enables teams to ask questions in plain English and get instant answers from their ERP, CRM, and database systems, eliminating days-long waits for reports. It emphasizes that effective AI integration embeds into existing workflows, allows non-technical users to generate reports naturally, and offers four implementation approaches from API-based to hybrid solutions. The business impact includes automated operations, faster decision-making, increased efficiency without added headcount, and competitive advantage through speed. AI integration has shifted from optional to essential for businesses wanting to eliminate reporting bottlenecks and enable self-service insights.
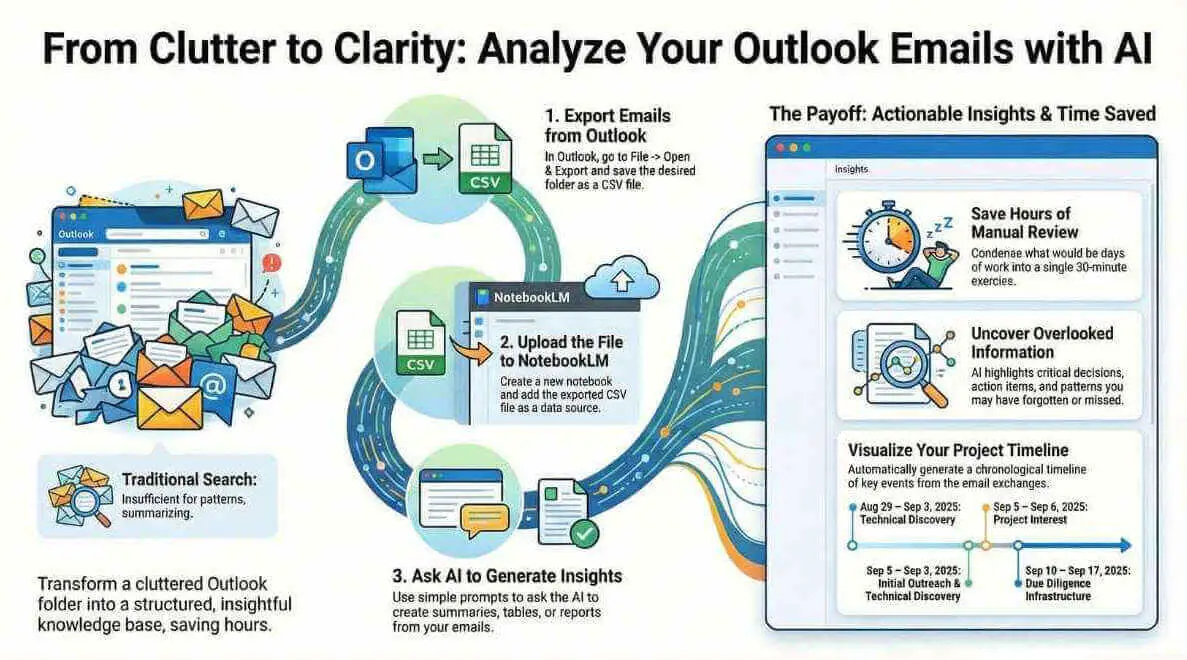
This article explains how to analyze Outlook email folders using NotebookLM AI to extract actionable insights from months of conversations. The simple process involves exporting emails as a CSV file, uploading to NotebookLM, and using AI prompts to generate organized summaries with key takeaways, decisions, and timelines. The tool automatically creates detailed analysis tables with verifiable citations linking back to source emails, saving hours of manual review. For recurring needs, the workflow can be automated using N8N to regularly analyze sales communications or project updates.
